When a Windows-based device fails to start up, several common issues can arise: misconfiguration in the BIOS/UEFI settings, hardware malfunctions, or software glitches. To simplify the troubleshooting process, it’s essential to understand how drives are configured and identify any errors encountered during startup.
Steps for Simplified Troubleshooting:
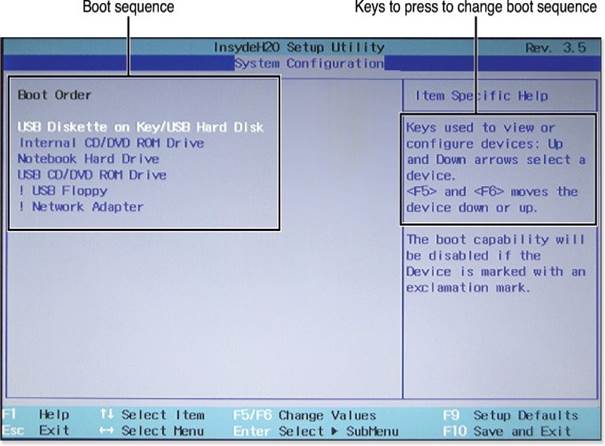
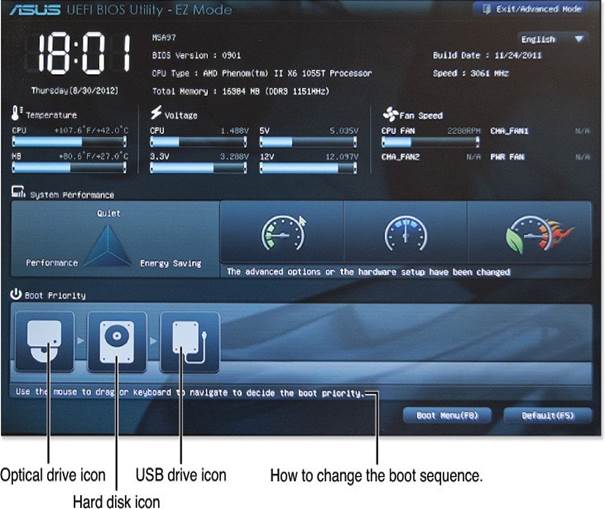
- Understand Drive Configurations: Examine how your device prioritizes bootable drives, such as hard drives (HDD), solid-state drives (SSD), or optical drives. This understanding helps in quickly isolating issues if a drive fails to boot.
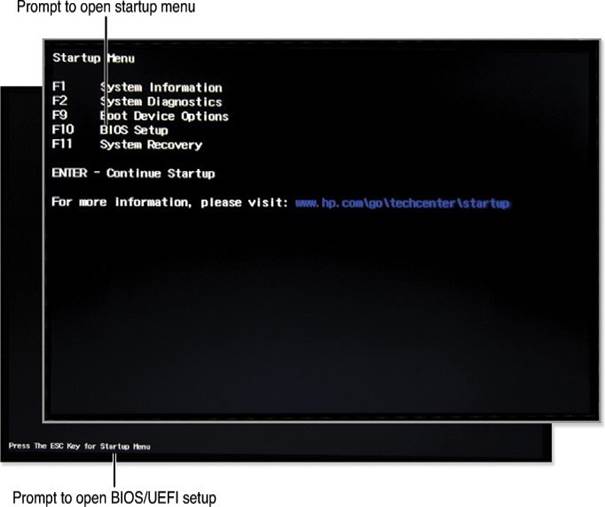
- Identify Startup Errors: After any changes, monitor the startup process for error messages that might point to hardware, software, or configuration issues.
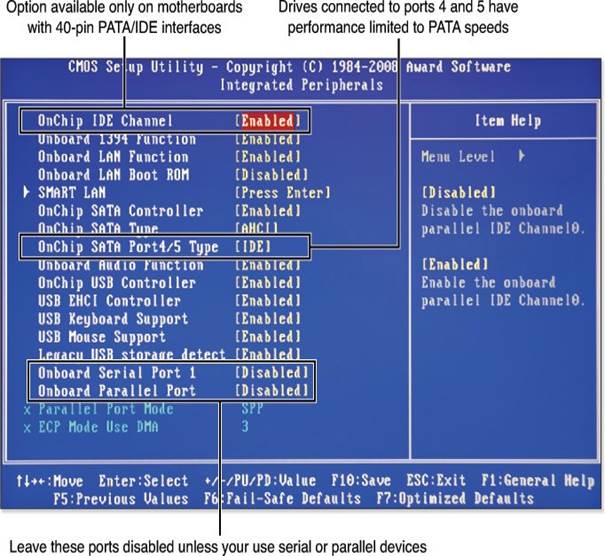
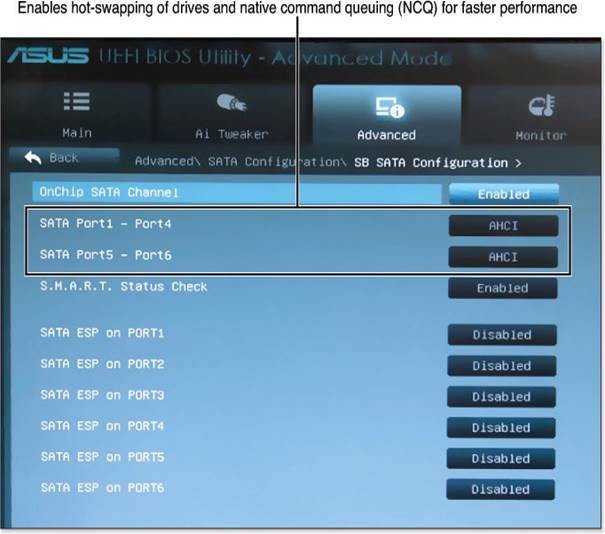
- Document BIOS Settings: While images of BIOS settings are not available here, you can still access and document these settings by navigating through your device’s BIOS/UEFI setup program. Focus on capturing boot order, drive configurations, and port settings to aid in troubleshooting.
- Utilize Tools for Analysis: While tools like Python scripts (as in the example below) can aid in analyzing configurations, they may be too technical for a general audience. Instead, consider using simple diagnostic tools or step-by-step guides that focus on visual analysis without coding.