To make the most of the tips in this section, you may need to change some settings on your wireless router. Here’s how to get started:
- Even if you usually connect to your router wirelessly, plug an Ethernet cable into one of the router’s ports and connect it to your computer. Most routers need a wired connection to change settings, even if some can be managed wirelessly.
- Open your web browser and type in your router’s IP address. If you don’t know what it is, check the instructions that came with your router. You can usually find a PDF or webpage from the router company.
- When prompted, enter the username and password. The default information is in your router’s instructions. If you’ve changed these, make sure to write them down somewhere.
To find your computer’s IP information, you can use the command prompt and type IPConfig/all. Look for the Default Gateway listed for your Ethernet connection; this is your router’s IP address.
To change wireless settings like the network name (SSID), security options, password, and channel, go to the Wireless Setup section.
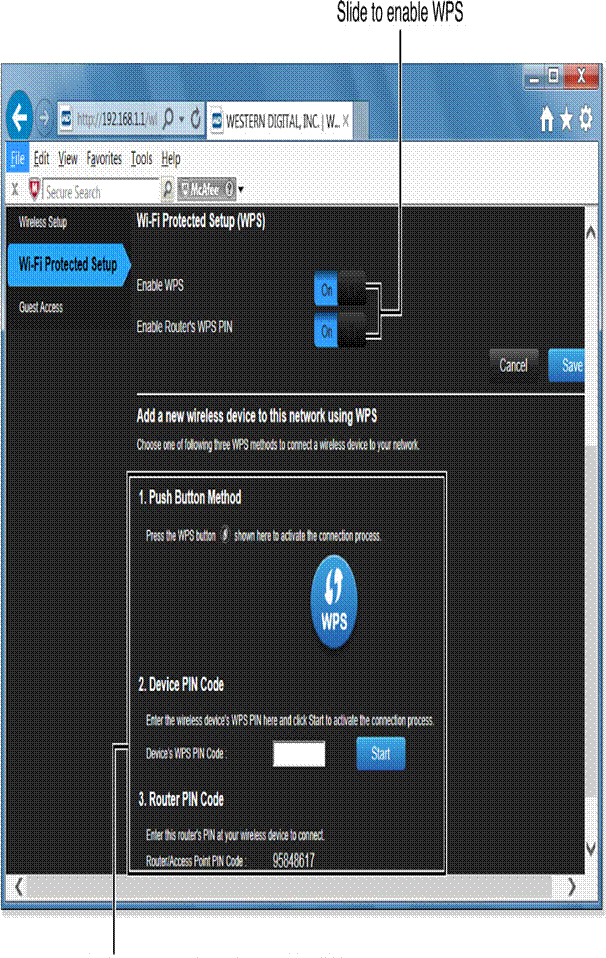
If you need to set up a device using WPS, go to the Wi-Fi Protected Setup section.
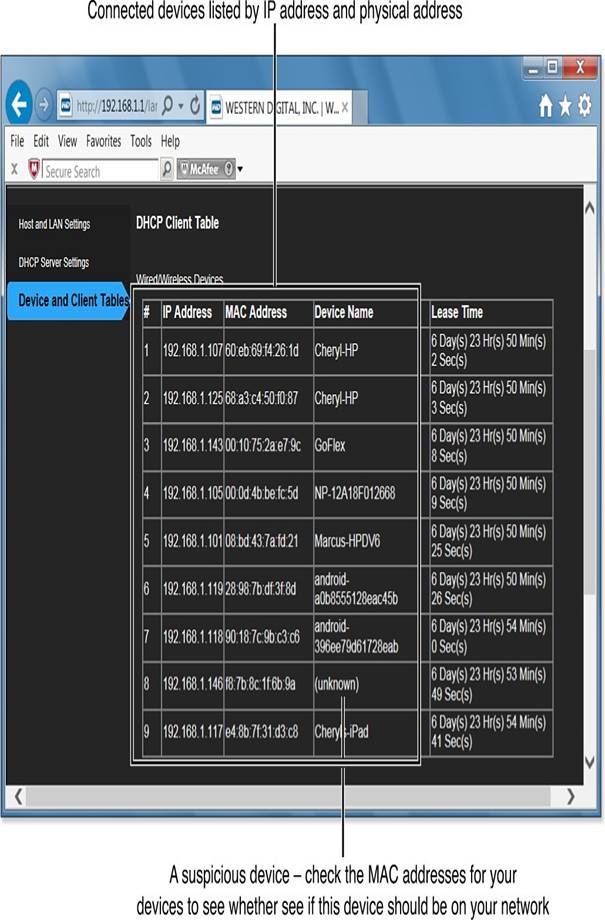
You can also check the Device and Client table to see the names and MAC addresses of devices connected to your network.
If some gaming systems are having trouble connecting to the Internet, you might need to set up port forwarding or allow direct Internet access for a specific device (known as DMZ). Look for these options in the advanced settings of your router.
After making your changes, remember to save them (some routers have a Save button at the bottom of the page) and close your browser. If you don’t usually use a wired connection, you can unplug the Ethernet cable from your computer but keep it connected to the router for future use.
Firmware Updates
Firmware is the software that controls how your router and mobile devices work. Updates to firmware can fix problems or add new features.
To update a smartphone or tablet, contact your service provider or the device maker.
For more details on updating, check the relevant section in your guide.
Updating Your Router
You can get firmware updates for your router from two places:
- The router manufacturer
- A third-party firmware provider, like DD-WRT
Getting Updates from the Manufacturer:
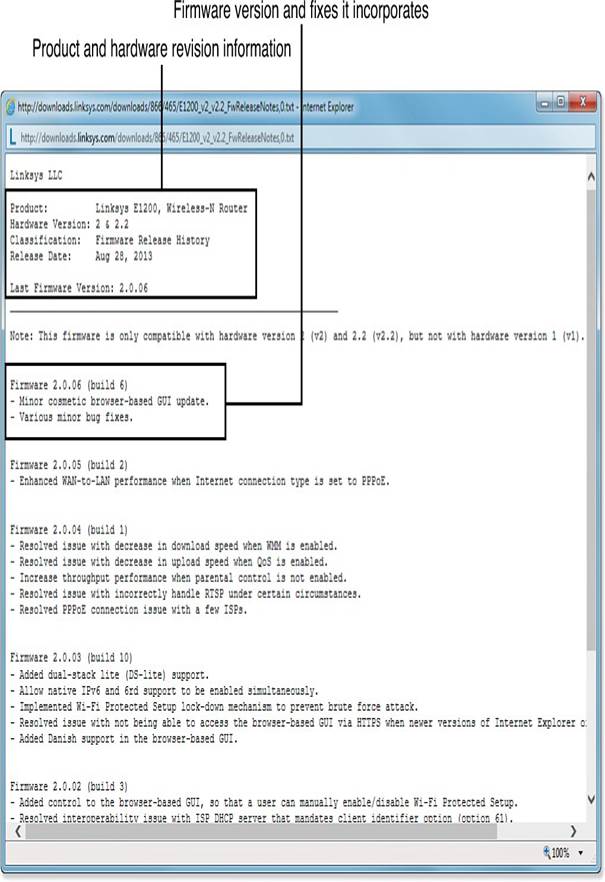
- Find the model and version number of your router, usually found on a label on the bottom or side. Different models may need different updates, so it’s important to know exactly which one you have.
- Log in to your router to check the current firmware version. This info is often on the login page or in the settings; refer to your router’s instructions for help.
- Visit the manufacturer’s website and go to the Support or Downloads section. Look for your router model to see available firmware updates and what issues they fix.
- If a new firmware version can solve your router problems, download it. The latest version usually includes all previous fixes.
- Before installing the new firmware, write down your current router settings. You can take screenshots or use a camera. This is important if you’ve changed the default login info or set up special features, as some settings might be lost during the update.
- Follow the instructions in your router’s documentation or on the website to install the firmware. You’ll likely need to log in with a wired connection. If your router has a USB port, you may need to copy the firmware update file to a USB drive.
- After the update, restart your router.
- Reapply any custom settings that may have changed during the update using the notes you made earlier.
Caution:
If the new firmware causes problems, you might want to try an earlier version. It’s best to update firmware only when it fixes a specific issue on your network, not just because a new version is available.
